Last Updated on October 15, 2021
Most drivers in the world have never driven a hybrid vehicle before. Only a small percentage understand that they run via an internal combustion gasoline engine and a battery-powered electric motor. But few of them know how this combination actually makes the car function.
The truth is that drivers get a choice between how much electricity from the electric motor they can use for their driving and the amount of gasoline they get from the internal combustion engine.
Normally, a driver would utilize both the engine and the electric motor in order to conserve both the battery power and gasoline. The battery inside of a hybrid vehicle is much larger than your typical conventional car battery but much smaller than one found in an electrical like a Tesla.
Not only does the hybrid battery have to power the basic accessories like the air conditioner and radio, it also must power some portion of the vehicle’s movement as well. This requires it to be much larger and more expensive than a typical car battery.
See Also: Pros/Cons of Hybrid Vehicles
Main Parts of a Hybrid Vehicle’s Internal Structure
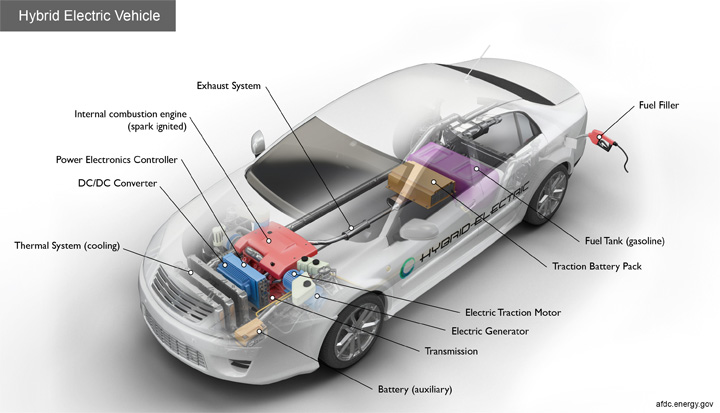
To understand how a hybrid vehicle works, you basically must understand its internal structure. While there are many components and systems that make up the parts of a hybrid vehicle, below are the 6 main parts of its structure.
#1 – Gasoline Engine
The hybrid vehicle still has a gasoline engine. This remains to be the main power source of the vehicle since 1 gallon of gasoline has the same energy as half a ton of battery power.
#2 – Electric Motor
This is the feature that makes the hybrid vehicle particularly special. The electric motor has the ability to accelerate the vehicle by taking power from the battery. However, it can also give power back to the battery if you slow down the vehicle.
#3 – Fuel Tank
You will still have a fuel tank to store your gasoline like in a conventional vehicle. Due to the advanced technology in hybrid cars, the gas won’t need to be used as much. You will have better fuel efficiency and produce fewer emissions as a result.
#4 – Transmission
Most hybrid vehicles will still use a conventional transmission that you would find in a regular gasoline car. However, there are new transmissions being built specifically for certain hybrid cars, such as the Toyota Prius.
#5 – Batteries
The batteries are what power the electric motor of a hybrid car. Not only that, but the batteries can actually take power back from the electric motor too. This is one way their lifespan can be preserved.
Read also: Average Lifespan of Hybrid Car Battery
#6 – Generator
If you have a series hybrid vehicle, they have a generator which gets powered by the gasoline engine. From there, the generator can then generate power for the electric motor and help recharge the battery. It is basically a way of converting gasoline into the electrical energy for the motor and battery.
Additional Information

Some hybrid vehicles can be plugged in for recharging the battery while others do not have this ability. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV) are considered to be electric vehicles while the ones you can’t plug-in are simply hybrid vehicles.
The ones you can plug in will typically have an “electric-only drive” feature which lets you power the movement entirely with the electric motor. The only problem is you can only drive at low speeds of between 10 and 30 miles per hour.
The electric motor is not powerful enough to accelerate the vehicle faster without tapping into the gasoline engine for more power. If you try to drive faster than 30 mph while on the “electric-only drive” mode, then you will exhaust your battery power quickly and then be forced to drive on only gasoline like in a normal car.




