Last Updated on June 24, 2022
If you’re a car enthusiast, you’ve probably heard of “drive-by-wire” technology. Drive-by-wire is a method of controlling a car’s throttle and brakes electronically, without the use of traditional mechanical linkages.
This technology is becoming increasingly common in new cars, and there are several advantages that come along with it. Here are 5 reasons why drive-by-wire technology is beneficial for car owners:
How Does Drive-by-Wire Technology Work?
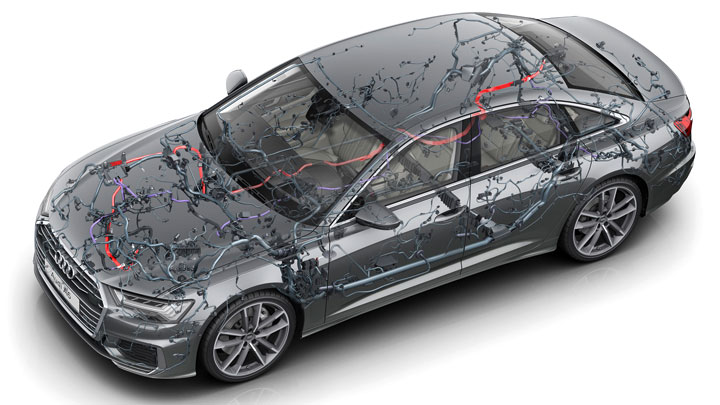
Drive-by-wire is a term used in the automotive industry that refers to a system where there is no mechanical linkage between the accelerator pedal and the engine. Instead, the accelerator pedal sends an electronic signal to a computer, which then sends a signal to the engine telling it how much power to produce.
This allows for more flexibility in how the car can be controlled, since different engines or even different motors can be used depending on what needs to be achieved. It also makes it easier to modify or update car control systems, since there is no need to change any of the underlying mechanical components.
Electronic controls are implemented into everything from the steering system to the braking system. There is even electronic throttle control as well.
See Also: 6 Cars That Use Brake-by-Wire Technology
Advantages of a Drive-by-Wire System

You will ultimately find that drive-by-wire technology requires fewer parts in vehicles than traditional mechanical cars. This creates a whole range of advantages for using one of these cars versus an old-style car.
#1 – Weight Reduction
Mechanically linked vehicles have lots of moving parts inside of them which adds extra weight. Drive-by-wire technology uses much fewer moving parts while reducing the weight of the vehicle at the same time.
#2 – Fuel Efficiency
With less moving parts, there is less demand for fuel. Since the electronics ultimately run off the car battery, this will result in much better fuel efficiency in your vehicle.
#3 – Fewer Carbon Emissions
This relates to the second advantage that was just talked about. Because there is fuel efficiency, this means your vehicle will be producing fewer carbon emissions. Those of you who care about the environment will surely appreciate this too.
#4 – Flexibility in Controls Placement
In a mechanical car, there are only a limited number of areas where controls can be placed in its interior. Drive-by-wire technology has changed this because it allows auto makers to place controls virtually anywhere that they want.
This gives drivers much better flexibility in how they control their vehicle while driving.
#5 – Safety Features
A computer which helps control a vehicle can be a huge benefit when it comes to adding safety to your driving experience. Drive-by-wire technology allows electronic safety systems to be added such as adaptive cruise control, blind spot detection, lane assistance, and electronic stability control. These are features you would never find in a mechanically controlled car.
Read Also: What Causes Cruise Control to Not Work
Are There Any Disadvantages to Drive-by-Wire Technology
The only worry that people seem to have about drive-by-wire cars is if the electronic components fail or get hacked. All it would take is for one computer or sensor in the vehicle to malfunction for there to be a major problem on the road.
However, the same thing could be said for a mechanical vehicle as well. All it would take is for one cable to break or something to happen to the hydraulic pressure for one of those vehicles to malfunction.
In actuality, drive-by-wire cars have so many safety features that you will know right away when some electronic component starts to malfunction. Then you can take it to the mechanic right away and fix the problem.
Drive-by-Wire vs Drive-by-Cable
The difference between a drive-by-wire and a drive-by-cable system is that with the former, there is little to no mechanical linkage between the accelerator pedal and the engine. In other words, in a drive-by-wire system there’s an electronic signal that tells the engine how much power it should make.
The latter (drive-by-cable) still relies on some form of mechanical cable to transfer data from the accelerator pedal to the engine. This type of system isn’t as common in newer cars, however it’s found in older vehicles.




