Last Updated on October 27, 2022
The engine of any vehicle depends on compressed air pressure to generate the power it needs to run properly. With a turbocharged or supercharged engine, the flow of air passes through each part first before heading into the vehicle’s engine.
This method of compressing outside air is referred to as forced induction and it can boost the power of the engine by as much as 50%. A turbocharger or supercharger are simply the two types of forced induction.
Related: 3 Types of Horsepower (and Why It Matters)
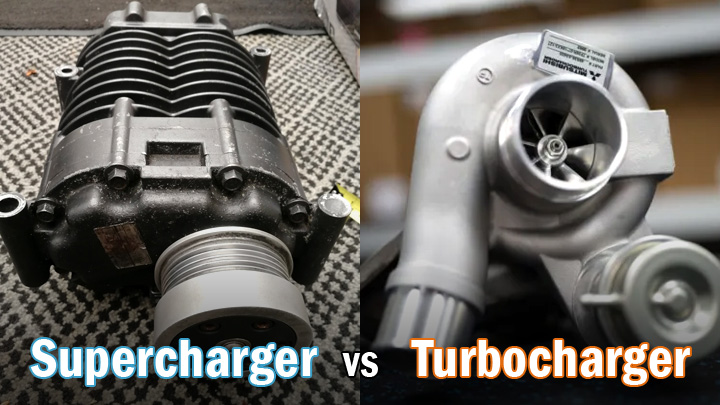
Difference Between a Supercharger and Turbo
A lot of people refer to these two systems interchangeably, but they actually have many differences. Although they are both essentially air compressors, the turbocharger depends on exhaust gasses to power it.
As for the supercharger, it simply needs power from the engine to run. Typically, the engine’s belt and crankshaft are what transmits this power effectively but different types of superchargers work differently.
The best way to know which is better for you is to compare the pros and cons of each type of forced induction system.
Related: P0299 Code (Underboost Condition)
Supercharger
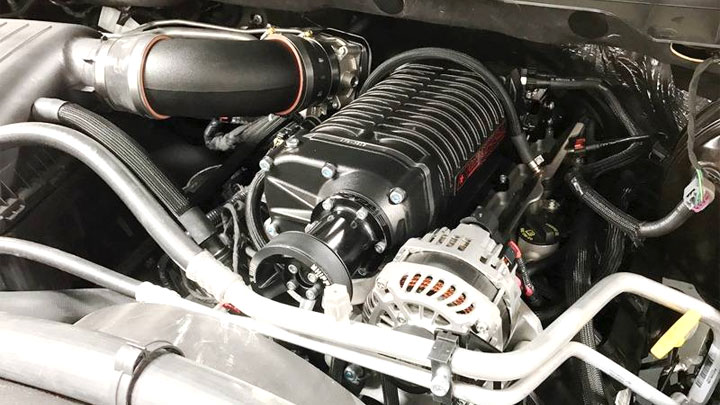

Below are the advantages and disadvantages of a supercharger (or blower).
Pros
- Lag is Nonexistent – The supercharger has power consistently delivered to it with no lag whatsoever. Since the crankshaft of the engine is always turning, then it is always able to deliver power to the supercharger.
- Low End Horsepower – Compared to a turbocharger, a supercharger will enable an engine to make more power at lower RPMs.
- Cost Effective – If you are looking for the most affordable forced induction system, then the supercharger is the cheaper option.
- Easier Installation – Superchargers have the ability to bolt on to almost any engine type.
Cons
- Less Reliable – Because of the higher temperatures and pressures that the interior of the engine is subjected to, the lifespan of the engine becomes affected. This means the longevity of the supercharger is also affected.
- Low Efficiency – Since the supercharger depends on engine power, this means it is taking away power from the engine even though it is producing more power for the engine.
- Noise – Superchargers have a noticeable whine when running. While this could be listed as a pro, most drivers prefer the almost silent operation of a turbocharger.
Read also: 5 Symptoms of a Bad Water Pump and Replacement Cost
Turbocharger
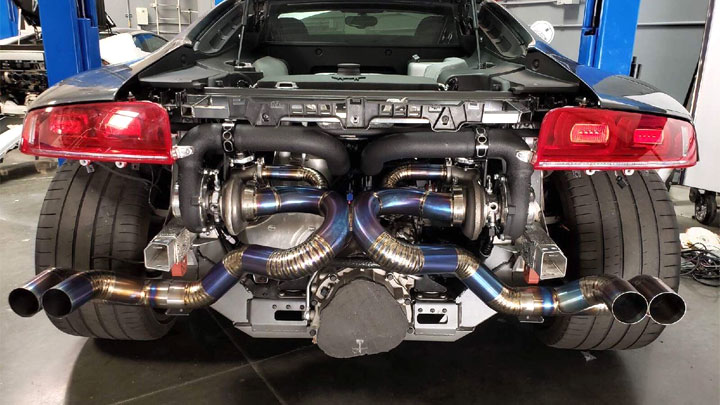

Below are the advantages and disadvantages of a turbocharger.
Pros
- Supports Smaller Displacements – If you have a smaller engine in your vehicle then the turbocharger will support its displacement. That way, you can generate additional power for an engine that is smaller.
- Top End Horsepower – There is a much greater increase in top-end horsepower when using a turbo compared to a supercharger.
- Good Efficiency – The exhaust gases of the turbine are what powers the turbocharger. These gases would normally be lost in a supercharger, but the turbocharger recovers them to provide the engine with better efficiency.
- Good Fuel Economy – Since smaller engines are used here, this means they use less fuel. Therefore, your fuel economy will be greatly improved.
Cons
- One RPM Range – Turbochargers are designed for one particular RPM range. This allows the flow of exhaust gasses to be good enough for providing more power to the engine.
- Lag – The power delivered to the turbocharger is not consistent because it depends on the presence of exhaust gasses from the turbine rather than a consistent crankshaft from the engine.
- Needs Engine Oil – Turbochargers tend to heat up quickly which means they will need to use engine oil just to stay lubricated. As a result, your engine oil will need to be changed more frequently.
- Surge – With many turbochargers, after they provide the biggest boost of power they can to the engine, there may be a power surge from it. This will cause problems with the tire traction and result in an unstable vehicle.
Related: What is Low Speed Pre-Ignition? (for Turbocharged Vehicles)